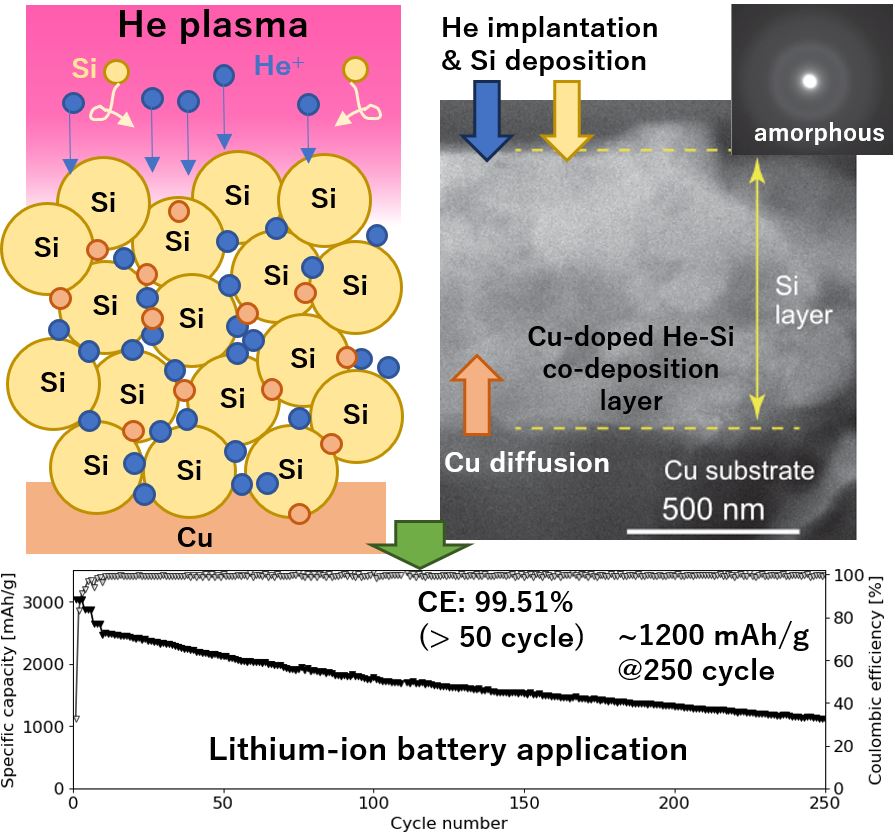
ヘリウムプラズマ中でのシリコンの堆積により、空孔率が約0.5のヘリウム-シリコン共堆積層を形成。この薄膜は、100~200nm前後の小クラスターと銅ドープを特徴とし、100サイクル後には1800mAh/gの放電容量を示しました。シリコン-ヘリウム共堆積法が高性能リチウムイオン電池用の多孔性アモルファスシリコン薄膜の作成の手法の1つとなることを示しています。
Silicon deposition in a helium plasma leads to a co-deposited helium-silicon layer with a porosity of ~0.5. This thin film, featuring small clusters around 100-200 nm and natural copper doping, demonstrates a discharge capacity of 1800 mAh/g after 100 cycles. This indicates that the silicon-helium co-deposition method is promising for creating porous amorphous silicon thin films for high-performance lithium-ion batteries.
Details can be found below:
Nanoporous Helium–Silicon Co‐Deposition Thin Film via Plasma‐Assisted Process for Lithium‐Ion‐Battery Anodes – Kajita – 2025 – Advanced Energy and Sustainability Research