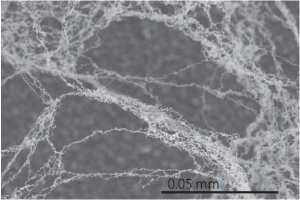
核融合炉では,壁材料が10 MW/m2という大きな熱と高エネルギーの粒子にさらされ,材料の損耗や変形が起こります。その超高熱流プラズマと壁材料相互作用に関する研究をダイバータ模擬装置での実験を中心に進めています。材料表面で起こるヘリウムプラズマ照射に伴う金属の綿毛化や,熱負荷に伴うアークの影響などを世界の拠点とネットワークをつくり明らかにしようとしています。
In a fusion reactor, wall materials are exposed to high heat (10 MW/m2) and high-energy particles, which cause erosion and deformation of the materials. We are studying the interaction between such a plasma and wall materials, mainly through experiments using divertor simulators. We are trying to clarify the metallic fuzz caused by helium plasma irradiation on the surface and the effects of arcs caused by heat loads by establishing a network with other centers around the world.
関連論文 (Related publication)
[1] Enhanced growth of large-scale nanostructures with metallic ion precipitation in helium plasmas
S Kajita, S Kawaguchi, N Ohno, N Yoshida
Scientific reports 8 (2018), 56
[2] Formation process of tungsten nanostructure by the exposure to helium plasma under fusion relevant plasma conditions
S Kajita, W Sakaguchi, N Ohno, N Yoshida, T Saeki
Nuclear Fusion 49 (2009), 095005